.png?width=576&height=265&name=The%20five%20modules%20of%20eCTD%20-%2002%20(2).png)
What are the five Modules of eCTD? - Introduction to the CTD Triangle
When talking about the electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD) topic, the five modules it consists of come up sooner or later. Why are they often depicted within the CTD triangle, and what information do life science companies have to provide to regulators within them when compiling their submissions in an eCTD format?
CTD vs. eCTD: similar content, different format
The content of an eCTD corresponds to the structure of its predecessor, the so-called Common Technical Document (CTD). This defines the structure and content of a paper submission. However, as the number of pages required for a dossier can quickly run into tens of thousands because of increasing regulation, the electronic Document Standard (eCTD) was developed. Due to the improved processing options available to companies and authorities, it is mandatory in many countries while its content is still oriented to the CTD.
The five modules of eCTD
An eCTD consists of five modules that are based on the structure of its predecessor, the CTD. The agreement to compile all quality, safety, and efficacy information in the CTD has transformed regulatory review procedures and enabled harmonized electronic submissions, facilitating the widespread implementation of good review practices. Furthermore, it removed industries’ need to reformat material for submission to multiple ICH regulatory authorities.
The CTD consists of five modules, often presented in a triangle showing how they are connected to each other. Module 1 at the top is region-specific, and Modules 2, 3, 4, and 5 are intended to be common for all regions. In July 2003, CTD became the mandatory format for new drug applications in the EU and Japan and the strongly recommended format of choice for New Drug Applications submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration.
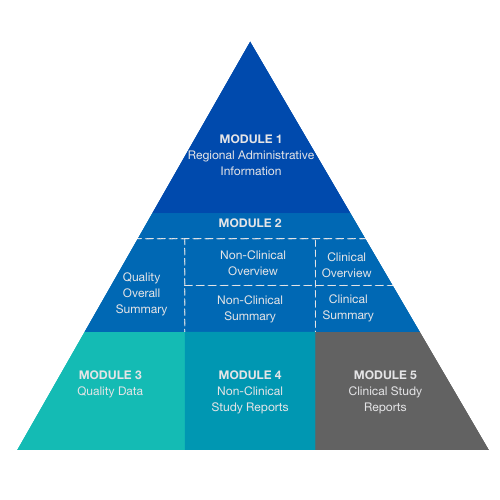
Module 1 – Regional Administrative Information
Module 1 contains information specific to the region to which the dossier is being submitted. The relevant regulatory authorities specify the content and format of this module. Module 1 of the eCTD (regional information) contains 3 three additional XML files (for each region). These contain include meta-information such as applicant, product, and submission date, as well as links to the files with the actual submission information.
Module 2 – Summaries
Module 2 contains summaries and overviews of the three CTD technical sections: Quality, Safety, and Efficacy. The organization of these summaries is described in separate guidance documents for each discipline (Quality, Safety, and Efficacy).
Module 3 – Quality
Module 3 contains information pertinent to the quality of the pharmaceutical substance and product. This consists of information concerning Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls of the drug/biologic biological substance and product.
Module 4 – Non-Clinical Study Reports
This module contains information on the non-clinical (pharmacological, pharmacokinetic, and toxicological) evaluation of the drug/biologic biological substance and product. This information is typically provided in the form of study reports and publications.
Module 5 – Clinical Study Reports
This module contains information on the clinical evaluation of the drug/biological product. This module typically includes Clinical Study Reports describing each conducted clinical study. Supportive publications are also provided here.
If you like to learn more about the story of the eCTD, please see our blog post: What is eCTD? - The story of the electronic Common Technical Document | EXTEDO
If you like to hear what our customers have to say about our solution eCTDmanager, please have a look at our interview with Glenn Robertson from Puma Biotechnology, who describes what benefits his company gained by using our software: EXTEDO eCTDmanager Customer Interview: Glenn Robertson, Puma Biotechnology - YouTube
.png)
%20(2).png)

